All the products TPI manufactures are based on customer designs and specifications. Once finished products leave TPI facilities, our customers install them on wind turbines or in electric vehicles. At the end of their life, the disposal of TPI manufactured parts remain the responsibility of our customers. As a manufacturing company, we recognize that while we may not oversee the final disposal of our product, it is still our responsibility to properly manage our material usage and waste production. We are committed to doing our part to increase material efficiency and recyclability, while continuing to pursue partnerships with industry consortia, OEMs, and academia on the circularity of wind blades and automotive parts.
Materials
Raw materials are the key cost driver of the products we manufacture. We aim to use our materials as efficiently as we can while still meeting the expectations and requirements of our customers. Our products are generally custom designed and built to the specifications of our customers. We currently track the materials used in our manufacturing processes through our product lifecycle management system and enterprise resource planning system. Approximately one percent of our materials used in 2023 were from renewable resources, balsa wood, and approximately three percent were from recycled sources, polyethylene terephthalate (PET). In addition, all facilities have chemical and hazardous waste management systems in accordance with laws and regulations in their respective regions.
Materials Recycling
Wind turbines are 85% to 90% recyclable, with the wind blade material constituting the remaining percentage that cannot be easily recycled, due to the nature of thermoset composites.14 Wind composite industry leaders, such as TPI, are focused on closing this recycling gap in order to reduce landfilling of wind energy waste. TPI is actively working toward creating sustainable end-of-life solutions by developing alternative uses for composite products reaching their end of life. We have led numerous projects to convert decommissioned wind blades into a variety of alternative uses including concrete products, cured in place pipe liners, recycled fiberglass yarns, construction panels, and structural flooring applications.
In addition to repurposing end-of-life composite products, TPI is working closely with industry and academic leaders to develop and implement solutions to enable circularity for thermoset composites. These solutions will allow for the recovery of high-quality composite materials such as glass fiber, carbon fiber, and core which can be reused in building wind blades, and other thermoset composite products. One collaboration we worked on during 2023 was with Northeastern University where a Life Cycle Assessment was conducted, and carbon footprints were calculated for various wind blade shredding techniques and recycling pathways such as pyrolysis and mechanical recycling.
We remain highly engaged in global efforts to reduce carbon emissions from our manufacturing operations, reduce waste, and implement pathways available for the reuse of as much of the waste we generate as possible. This year we participated in the preparation of five new project proposals that have been awarded by the US Department of Energy focused on wind blade recycling and sustainable materials which we will begin working on during 2024.
Waste
Mitigating and managing waste generated from production is a key objective for TPI. Our facilities manage the waste generated according to local regulations. Our waste data is collected monthly using invoices from disposal facilities and haulers. All waste data is verified by on site EHS supervisors and through annual audits conducted at our ISO 14001 certified facilities. These processes allow TPI to understand the volume and cost of waste produced to ensure waste reduction remains a priority.
We have waste continuous improvement teams at each location, which completed waste stream analyses and developed waste reduction projects.
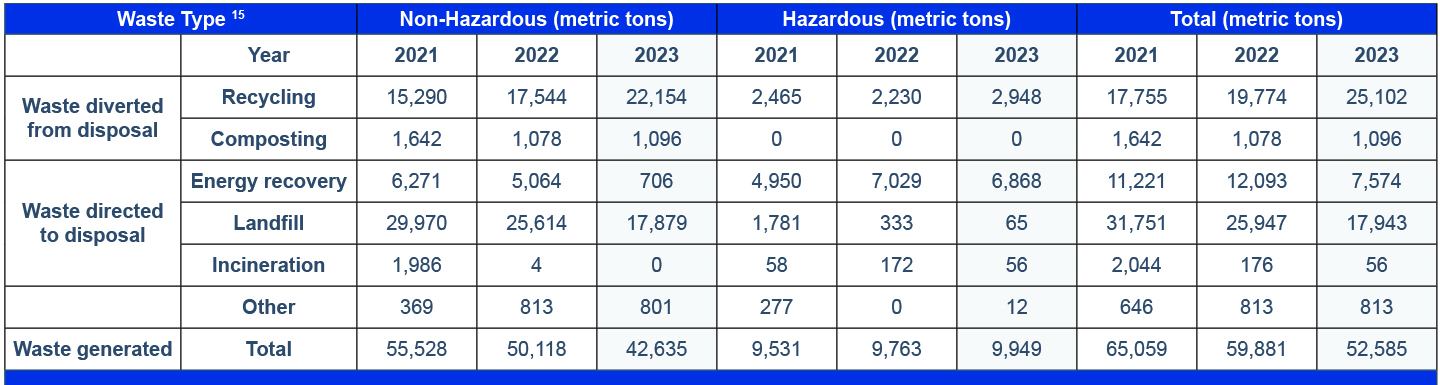
In a continuation of our program, in 2023, we achieved our waste rate reduction goal (5% reduction during the year) by focusing our projects on optimizing direct material usage. During 2023, both of our Türkiye sites achieved zero waste to landfill as shown in the reduction in total waste sent for landfill in the table below. In the coming years, our main focus is to encourage all sites to adopt alternative waste disposal methods instead of relying on landfilling.
This year, we had 52,585 metric tons of waste, of which 9,949 metric tons was hazardous and 42,635 metric tons was nonhazardous waste. Landfilled hazardous waste is disposed of through controlled confinement in a landfill that is lined, monitored, and in compliance with government regulations.
14 Circular Economy: Blade recycling is a top priority for the wind industry | Wind Europe
15 Hazardous waste disposal methods are confirmed by hazardous waste manifests. Non-hazardous waste disposal methods are confirmed based on vendor reports. Waste is reported based on shipment dates from our facilities. The other category includes waste disposed from cafeteria grease traps and using the U.S. EPA H141 code that is stored by the waste vendor and the disposal method is not provided to TPI.
