TPI’s commitment to safety remains our number one Core Value. To enable a culture of safety, our environmental, health, and safety (EHS) programs are managed by a global team of trained professionals with extensive knowledge and experience in all aspects of EHS. These global teams manage the following activities:
- Behavior Based Safety (BBS) program
- EHS action teams
- Good-catch safety program
- Weekly safety walks
- Daily safety communications
- Safety education
- Safety committees and inspections
- Risk assessments
- Job safety analysis
Along with EHS leadership teams, safety committees have been implemented at all sites. These committees allow associates to participate in the improvement of their facility’s safety management through monthly meetings. Committee responsibilities include the review of safety incidents, identification of safety hazards, follow-up on safety improvement action plans and more.
Additionally, each of our manufacturing facilities have deployed EHS Action Teams. EHS Action Teams are small cross-functional teams of associates performing proactive EHS activities to drive continuous improvement. These teams work on projects relating to ergonomics, risk assessment, job safety analysis, and EHS inspections. At TPI, associates have access to non-occupational medical and healthcare services which vary across our facilities. These services include on-site clinics, referral to outside medical services, and private health insurance. Voluntary health promotions also vary between facilities but include preventative wellness checks, fitness and wellness benefits, healthy eating programs and more.
This year, we launched the Global Safety Kaizen Week, as part of TPI’s LEAN program. “Kaizen” is a Japanese term meaning “change for the better.” During the Kaizen week, associates and corporate leadership collaborated over several days to brainstorm solutions to ongoing EHS challenges, leading to process improvements. Cross-functional teams at each site participated to reduce risk, implement continuous improvements, demonstrate leadership commitment, and foster associate engagement. Projects completed included mitigating equipment hazards, addressing ergonomic challenges, and reducing waste.
EHS Management
We continue to align safety practices across our global facilities and utilize ISO 45001 Certifications to standardize and strengthen our EHS Management Systems. To ensure continued compliance with our ISO 45001 certifications, our sites receive third-party surveillance audits on an annual basis and a full management system audit every three years. In 2024, we introduced two new EHS policies to uphold our commitment to safety and continuous improvement. Policies implemented this year included the Heat-Related Illness Prevention Policy, and Fire Protection and Prevention, and Hot Work Policy. These policies established new requirements and procedures to ensure the continued well-being of personnel on-site.
TPI also utilizes a third-party tool to identify and assess EHS legal requirements. The third-party tool monitors new or changes to existing regulations and facilitates audits of our activities to ensure compliance. When gaps are identified, action plans are developed by site EHS teams. Each month, corporate EHS meets with the sites to review the EHS compliance register for accuracy, consistency, and to provide support for any escalated items.
Safety Communication and Education
Safety communication materials are provided to associates and discussed with leadership. Topics include recent safety hazards, issues, and training. Furthermore, associates can remove themselves from any situation they view to be hazardous to their health without fear of retaliation. Corrective action to perceived hazards are implemented as appropriate by TPI. We further ensure the safety of our associates to support our zero-harm culture through safety education. Safety education is the foundation for our other safety measures. Associates receive regular training on environmental, health, and safety related topics. This training includes but is not limited to:
- General awareness EHS training
- Ergonomics training
- Compliance training
- Hazard-specific training as required for the job or task
- Fire hazard and prevention training
- Hazardous material training
- Equipment-specific safety training
- Safety incident and corrective action training
Incident Prevention
We have implemented several programs at our facilities to prevent and manage incidents. During weekly safety walks, members of the facility leadership team observe operations to identify unsafe conditions and unsafe behaviors while engaging with associates to verify their EHS knowledge and coaching them on observed behaviors. Our standard global BBS process also ensures we provide coaching around at-risk behaviors and reinforce safe behaviors. These observations focus on correct PPE usage, ergonomic postures, equipment handling, and daily manufacturing safety procedures. In 2024, our facilities completed more than 6,600 observations.
While we employ various preventative safety measures across our operations, we understand that accidents may happen and have processes in place to investigate and prevent future injuries. EHS-related incidents are reported via a robust and standardized software solution. When an incident occurs, it is immediately communicated to senior management. Then a root cause is identified, and corrective actions are implemented to address the hazard that led to the incident. All safety information is tracked and reviewed at each facility and with the leadership team. Incidents and corrective actions are then shared across facilities, along with significant good-catches, to ensure that best practices are implemented globally. A good-catch is the identification of a condition or behavior that has the potential to cause harm with timely intervention and corrective action before an incident occurs. In 2024, the number of good-catches submitted was more than 21,700.
Safety Performance
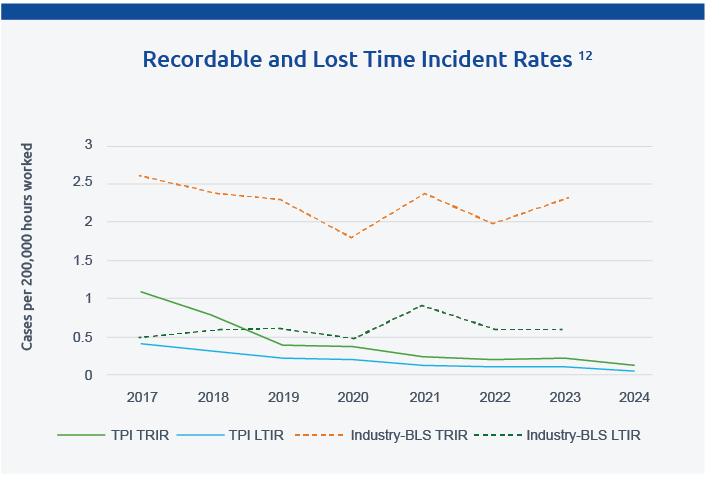
Our safety program consistently outperforms industry standards and remains best in class, with our 2023 and 2024 Total Recordable Incident Rate (TRIR) and Lost Time Incident Rate (LTIR) well below the rates reported by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. In 2024, we achieved our goals for TRIR and LTIR, which were set to remain below 0.24 and 0.13 respectively.11
Chemical Management
All TPI facilities have chemical management policies and procedures in accordance with laws and regulations in their respective regions. Chemical management procedures detail the proper handling, storage, and disposal methods for chemical products at the facility. TPI’s chemical management programs include maintaining and updating safety data sheet inventories for all chemicals and implementing strict emergency response plans. All chemicals entering and exiting TPI facilities follow labeling requirements in accordance with strict regulations to properly identify chemical properties that pose major hazards including flammability, corrosiveness, and toxicity. For a new chemical to be approved to enter a TPI facility it must follow a chemical approval process which includes an in-depth review by EHS departments. In addition, TPI uses a third-party chemical management solution which allows us to review chemicals in our inventory against regulatory reports as well as anticipate changes in chemical regulation before they happen.
Management of hazardous chemical waste is also extremely important to TPI since our manufacturing process deals with these substances. At all TPI manufacturing sites, hazardous waste policies and procedures have also been implemented. These procedures include the identification, labeling, disposal, containment, and storage of hazardous wastes. In addition to strategic chemical programs, associates that may encounter chemical or physical hazards and waste materials are trained on chemical labeling and handling, detecting hazards, and understanding safety data sheets, and emergency procedures. TPI’s commitment to associate safety goes beyond training as all our locations follow requirements for Industrial Hygiene by monitoring associate exposures when working with hazardous materials. A majority of our EHS teams utilize third-party organizations that help TPI identify hazards, perform exposure monitoring, and set up action plans to reduce risks to chemical, noise, dust, and heat exposures.
11 Number of incidents per 100 associates. Incident Rate (IR) = Number of Incidents X 200,000/Number of Associate Labor Hours. Injury frequency rates calculate the number of injuries per year for each 1 million hours worked. Recordable incidents are based on OSHA reporting requirements and exclude first-aid injuries. Injury Frequency Rate (IFR) = Number of Injuries X 1,000,000 /Number of Associate Labor Hours.
12 Industry incident rates are according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Survey of Occupational Injuries and Illnesses NAICS code 333611
